what happens to microplastics when they are ingested?
Australians are eating and inhaling significant numbers of tiny plastics at habitation, our new enquiry shows.
These "microplastics", which are derived from petrochemicals extracted from oil and gas products, are settling in dust effectually the house.
Some of these particles are toxic to humans — they can carry carcinogenic or mutagenic chemicals, pregnant they potentially cause cancer and/or damage our Deoxyribonucleic acid.
We still don't know the truthful bear upon of these microplastics on homo health. But the adept news is, having difficult floors, using more natural fibres in clothing, effects and homewares, forth with vacuuming at least weekly can reduce your exposure.
What are microplastics?
Microplastics are plastic particles less than five millimetres across. They come from a range of household and everyday items such as the dress we wear, home effects, and food and beverage packaging.
We know microplastics are pervasive outdoors, reaching remote and inaccessible locations such as the Chill, the Mariana Trench (the globe's deepest bounding main trench), and the Italian Alps.
Our written report demonstrates it's an inescapable reality that we're living in a body of water of microplastics — they're in our food and drinks, our oceans, and our homes.
Baca juga: We gauge up to 14 meg tonnes of microplastics lie on the seafloor. It's worse than nosotros thought
What nosotros did and what nosotros found
While research has focused mainly on microplastics in the natural environment, a handful of studies have looked at how much we're exposed to indoors.
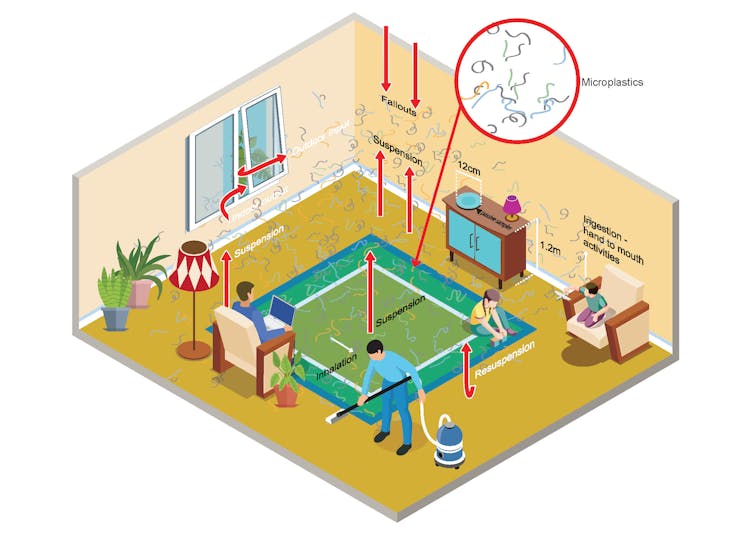
People spend up to xc% of their time indoors and therefore the greatest risk of exposure to microplastics is in the home.
Our written report is the first to examine how much microplastic we're exposed to in Australian homes. We analysed dust deposited from indoor air in 32 homes across Sydney over a ane-month menses in 2019.
We asked members of the public to collect grit in especially prepared drinking glass dishes, which we so analysed.
We found 39% of the deposited dust particles were microplastics; 42% were natural fibres such as cotton, hair and wool; and 18% were transformed natural-based fibres such equally viscose and cellophane. The remaining 1% were film and fragments consisting of various materials.
Betwixt 22 and vi,169 microfibres were deposited every bit grit per square metre, each day.
Homes with carpet as the main flooring covering had nearly double the number of petrochemical-based fibres (including polyethylene, polyamide and polyacrylic) than homes without carpeted floors.
Conversely, polyvinyl fibres (synthetic fibres made of vinyl chloride) were ii times more prevalent in homes without carpet. This is considering the coating applied to hard floor degrades over time, producing polyvinyl fibres in house dust.
Microplastics can be toxic
Microplastics can behave a range of contaminants such as trace metals and some potentially harmful organic chemicals.
These chemicals can leach from the plastic surface one time in the body, increasing the potential for toxic furnishings. Microplastics can have carcinogenic backdrop, meaning they potentially cause cancer. They tin as well be mutagenic, meaning they can damage DNA.
Baca juga: Why ocean pollution is a clear danger to man health
However, even though some of the microplastics measured in our written report are composed of potentially carcinogenic and/or mutagenic compounds, the bodily risk to homo wellness is unclear.
Given the pervasiveness of microplastics not only in homes but in food and beverages, the crucial adjacent pace in this research expanse is to establish what, if any, are prophylactic levels of exposure.
Baca juga: You're eating microplastics in ways you don't even realise
How much are we exposed to? And can this exist minimised?
Roughly a quarter of all of the fibres nosotros recorded were less than 250 micrometres in size, pregnant they can be inhaled. This ways we can be internally exposed to these microplastics and any contaminants fastened to them.
Using man exposure models, we calculated that inhalation and ingestion rates were greatest in children under six years old. This is due to their lower relative body weight, smaller size, and higher breathing rate than adults. What's more, young children typically have more than contact with the floor, and tend to put their easily in their mouths more oftentimes than adults.

Children under six inhale effectually iii times more than microplastics than the average — 18,000 fibres, or 0.3 milligrams per kilogram of trunk weight per year. They would too ingest on boilerplate 6.1 milligrams of microplastics in dust per kg of body weight per twelvemonth.
For a 5-year-old, this would be equivalent to eating a garden pea's worth of microplastics over the form of a year. Merely for many of these plastics there is no established safe level of exposure.
Our study indicated there are effective ways to minimise exposure.
Offset is the choice of flooring, with hard surfaces, including polished wood floors, likely to have fewer microplastics than carpeted floors.
Too, how frequently y'all make clean makes a difference. Vacuuming floors at least weekly was associated with less microplastics in dust than those that were less frequently cleaned. And so get cleaning!
Source: https://theconversation.com/were-all-ingesting-microplastics-at-home-and-these-might-be-toxic-for-our-health-here-are-some-tips-to-reduce-your-risk-159537
0 Response to "what happens to microplastics when they are ingested?"
Publicar un comentario